
Jacob Grimm
(1785 - 1863)
Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm – famous for their classical collections of folk songs and folktales, especially for Kinder- und Hausmärchen(Children's and Household Tales); generally known as Grimm's Fairy Tales, which helped to establish the science of folklore. Stories such as 'Snow White' and 'Sleeping Beauty' have been retold countless times, but they were first written down by the Brothers Grimm. In their collaboration Wilhelm selected and arranged the stories, while Jacob, who was more interested in language and philology, was responsible for the scholarly work. The English writer Ford Madox Ford sees in his masterly guide The March of the Literature (1938) that their tales were more than a mere reflection of German romanticism:

"But the real apotheosis of this side of the Teutonic cosmos came into its own through the labors of the brothers Ludwig Karl, and Wilhelm Karl Grimm for whom the measure of our administration may well be marked by the fact that there is nothing in the world left to say about their collection of fairy tales. It is, on the whole, wrong to concede the brothers Grimm to the romantics. They belonged to the earth movement and are known wherever the sky covers the land. That is the real German Empire."

Jacob Grimm was born in Hanau. His father, who was educated in law and served as a town clerk, died when Jacob was young. His mother Dorothea struggled to pay the education of the children. With financial help of Dorothea's sister, Jacob and Wilhelm were sent to Kasel to attend the Lyzeum. Jacob then studied law at Marburg. He worked from 1816 to 1829 as a librarian at Kasel, where his brother served as a secretary. Between 1821 and 1822 the brothers raised extra money by collecting three volumes of folktales. With these publications they wanted to show, that Germans shared a similar culture and advocate the unification process of the small independent kingdoms and principalities.
Altogether some 40 persons delivered tales to the Grimms. Probably the German writer Clemens Bretano first awoke their interest in folk literature. Their first tales date from 1807. The the most important informants included Dorothea Viehmann, the daughter of an innkeeper, Johann Friedrich Krause, an old dragoon, and Marie Hassenpflug, a 20-year-old friend of their sister, Charlotte, from a well-bred, French-speaking family. Marie's stories blended motifs from the oral tradition and Perrault's Tales of My Mother Goose (1697).
The brothers moved in 1830 Göttingen, Wilhelm becoming assistant librarian and Jacob librarian. In 1835 Wilhelm was appointed professor, but they were dismissed two years later for protesting against the abrogation of the Hannover constitution by King Ernest Augustus. In 1841 they became professors at the University of Berlin, and worked with Deutsches Wörterbuch. Its first volume came out in the 1850s; the work was finished in the 1960s.
The Grimms made major contributions in many fields, notably in the studies of heroic myth and the ancient religion and law. They worked very close, even after Wilhelm married in 1825. Jacob remained unmarried. Wilhelm died in Berlin on December 16, 1859 and Jacob four years later on September 20, 1863. He had just finished writing the dictionary definition for Frucht.
The Grimms came over a century after Madame d'Aulnoy and Charles Perrault, who between them first created and popularized the literary fairy tale. Grimms were more intent on capturing the genuine oral tradition – earlier Ludwig Tieck and Johann-Karl Musaeus relied more on the gothic tradition than folklore. In English Grimms' Tales are often referred as "fairytales", but only a few of them involve mythical creatures. The first English translation appeared anonymously in 1823, under the title German Popular Stories, translated from the Kinder und Haus Märchen, collected by M.M. Grimm, from Oral Tradition. It was the work of the London lawyer Edgar Taylor and his collaborator David Jardine. Noteworthy, this edition was illustrated by George Cruikshank; Jacob and Wilhelm themselves followed the example and encouraged their younger brother Ludwig Emil to illustrate the Kleine Ausgabe (1825). After its appearance, the Talesbecame to be regarded as a children's book.
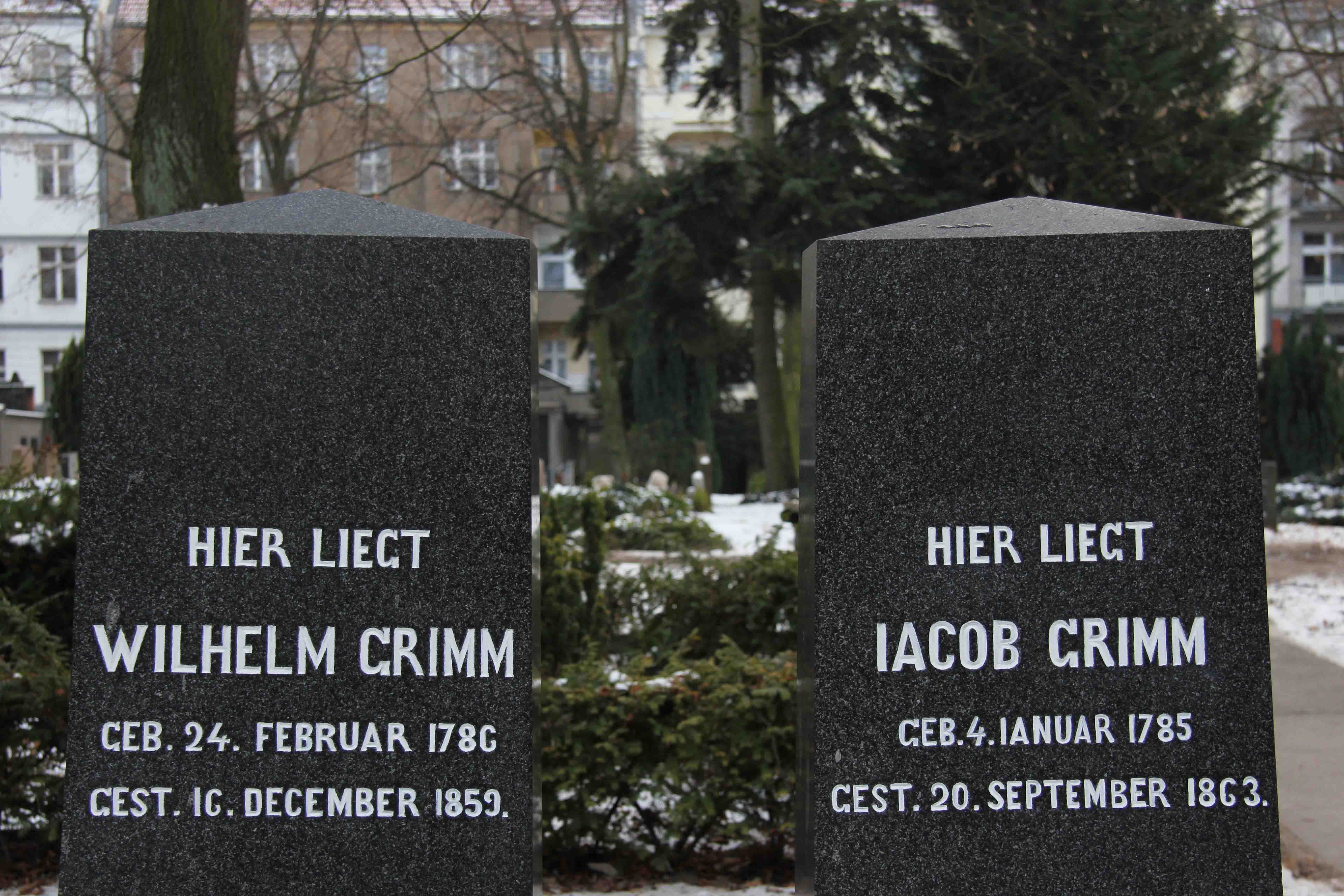
Kinder- und Hausmärchen was published in two volumes (1812-1815). In 1810 they had sent to Bretano brief summaries of the tales, but when his plans to publish an edition of fairy tales never realized, they turned to Achim von Arnim, who encouraged the brothers to publish their own collection. The final edition was appeared in 1857 and contained 211 tales; a further 28 had been dropped from earlier editions, making 239 in total. The Grimms wrote down most of the tales from oral narrations, collecting the material mainly from peasants in Hesse. The first edition included stories in 10 dialects as well as High German. Among the best-known stories are 'Hansel and Gretel,''Cinderella,''Rumpelstiltskin,''Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs,' and 'The Golden Goose.' The stories include magic, communication between animals and men, and moral values, teachings of social wright and wrong. Critics complained, that some of the tales were not appropriate for children, who nevertheless were fascinated by their grim magic: "What a tender young creature! what a nice plump mouthful – she will be better to eat than the old woman." (from 'Little Red-Cap')
The brothers are generally treated as a team, though Jacob concentrated on linguistic studies and Wilhelm was primarily a literary scholar. Jacob wrote down most of the tales published in the first volume. From 1819 onward, Wilhelm supervised all subsequent editions on his own, because Jacob was repeatedly away on diplomatic missions. During the editing phase they constantly consulted each other.
The Grimms' were affected by the ideas of Enlightenment and the German Romanticism and its interest in mythology, folklore and dreams. Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm argued that folktales should be collected from oral sources, which aimed at genuine reproduction of the original story. Their method became also model for other scholars. However, in practice the tales were modified, and in later editions of the fairytales Wilhelm's editing and literary aspiration were more prominent.
From his first book, Über den altdeutschen Meistergesang (1811) Jacob Grimm supported the theory about the unique relationship between the 'original' German language and the folktales, whose origins were coeval with the origins of German culture.
While collaborating with Wilhelm Jakob turned to study of philology, producing the Deutsche Grammatik. Jakob's views on grammar influenced deeply the contemporary study of linguistics, Germanic, Romance, and Slavic. The work is in use even now. In 1822 Jacob devised the principle of consonantal shifts in pronunciation known as Grimm's Law. He illustrated the changes in Germanic by citing contrasting cognates in Latin, Greek, or Sanskrit.
In Jacob Grimm's Deutsche mythologie fairy tales are traced in the pre-Christian era, in ancient faith and superstitions of the Germanic peoples. The archaic pre-medieval Germany was seen representing a Golden Age, a period of comparative harmony and happiness before it was lost. This romantic view of the history owed much to Bible's tale of Eden or perhaps also Arthurian legends.
Both brothers argued that folktales should be recorded and presented in print in a form as close as possible to the original mode. It also meant that some of the stories contained unpleasant details. Doves peck out the eyes of Cinderella's stepsisters, and in 'The Juniper Tree' a woman decapitates her stepson. A witch kills her own daughter in 'Darling Roland.'"These stories are suffused with the same purity that makes children so marvelous and blessed," wrote Wilhelm Grimm in the preface to the Nursery and Household Tales. In practice the brothers modified folktales in varying ways, sometimes even intensifying violent episodes. Especially references to sexuality embarrassed the Grimms'. In 'The Snow White' the violence was toned down by later editions: at the end of the story the wicked Queen is forced to put on red-hot iron slippers and dance till she dies. The witch ends up in the oven and is baked alive in 'Hansel and Gretel.' At the end of World War II, allied commanders banned the publication of the Grimm tales in Germany in the belief that they had contributed to Nazi savagery. For a long period, the tales were largely banned from the German nursery, but in 2012 the 200th anniversary of the publication of Die Kinder und Hausmärchen launched the 2013 celebrations of the brothers.

For further reading: Grimm Brothers and the Germanic Past, ed. by Elmer H. Antonsen (1990); The Hard Facts of the Grimms' Fairy Tales by Maria M. Tatar (1990); The Brothers Grimm and Folktale, ed. by James M. McGlathery (1991); The Brothers Grimm and Their Critics by Christa Kamenetsky (1992); Grimms' Fairy Tales by James M. McGlathery (1993); The Reception of Grimms' Fairy Tales, ed. by Donald Haase (1993); The Brothers Grimm: Two Lives, One Legacy by Donald R. Hettinga (2001) William Butler Yeats (1865-1939) studied Irish legends and tales, which he published with George Russell and Douglas Hyde in Fairy and Folk Tales of the Irish Peasantry (1888). Although Grimm's Fairy Tales is in fact much closer to genuine folk tales, the Brothers Grimm probably rival Hans Christian Andersen as the best-known tellers of fairy tales. Their stories have been utilized by many modern fantasists, including Tanith Lee, Robin McKinley, and Patricia Wrede. Film: The Wonderful World of the Brothers Grimm (1962), dir. by Henry Levin, George Pal, starring Laurence Harvey, Karl Boehm, Claire Bloom, Barbara Eden - an account of the lives of the brothers, supplemeted by three stories, "The Dancing Princess,""The Cobbler and the Elves," and "The Singing Bone.

Selected works:
- Über den altdeutschen Meistergesang, 1811
- Die beiden ältesten deutschen Gedichte aus dem achten Jahrhundert: das Lied von Hildebrand und Hadubrand und das Weissenbrunner Gebet, 1812 (ed., with Wilhelm Grimm)
- Kinder- und Hausmärchen, 1812-15 (2nd. ed. 1819, 3rd. ed. 1837, 4th ed. 1840, 5th ed. 1843, 6th ed. 1850, 7th. ed. 1857)- German Popular Stories (translated by Edgar Taylor, illustrated by George Cruikshank, 2 vols., 1823-1826) / Household Tales (tr. 1853, illustrated by H. Wehnert) / Grimm's Fairy Tales (translated by H.B. Paull, 1868) / Household Tales (tr. 1884) / Household Stories (translated by Lucy Crane, 1886) / Household Fairy Tales (translated by Ella Bodley, 1890) / Tales (translated by Wanda Gág, 1936) / German Folk Tales (translated by Francis P. Magoun Jr. and Alexander H. Krappe, 1960) / Fairy Tales (translated by James Stern, 1972) / Grimm's Tales for Young and Old, 1977 (translated by Ralph Manheim, 1977) / Fairy Tales (translated by Jack Zipes, 1987)Altdeutsche Wälder, 1813-1816 (3 vols., ed., with Wilhelm Grimm)
- Deutsche Sagen, 1816-1818 (with Wilhelm Grimm; 2 vols.)- The German Legends of the Brothers Grimm (translated by Donald Ward, 1981)
- Deutsche Grammatik, 1819-37 (4 vols.)
- Deutsche Rechts Alterhümer, 1828
- Deutsche mythologie, 1835- Teutonic Mythology (translated by James Steven Stallybrass, 1883-1885)
- Geschichte der deutschen Sprache, 1848 (2 vols.)
- Deutsches Wörterbuch, 1852-1961 (with Wilhelm Grimm, 16 vols., 32 bound in pairs)
- Kleinere Schriften, 1864-1890 (8 vols.)
- Briefe der brüder Grimm, 1923 (ed. H. Gürtler)
- Die schönsten Grimms Märchen, 1950 (ed. Gisela Fischer)- Tunnettuja Grimmin satuja (suom. Leena Niukkanen, 1979)
- Reden und Aufsätze, 1966 (ed. W. Schoof)
- Die allerschönsten Märchen der Gebrüder Grimm, 2004 (illustrated by Bernhard Oberdieck)

